Electrocatalytic Technology
The energy and wastewater treatment sectors are currently facing a dual challenge: the need to decarbonize hydrogen production and the obligation to efficiently treat nitrogen‑rich wastewater.
- Current bottleneck: Conventional electrolysis technologies rely on materials that are either too expensive (noble metals such as platinum) or insufficiently durable and inefficient at high current densities.
- The opportunity: Leveraging urea present in industrial and municipal effluents as a fuel source to produce hydrogen at significantly reduced energy cost.
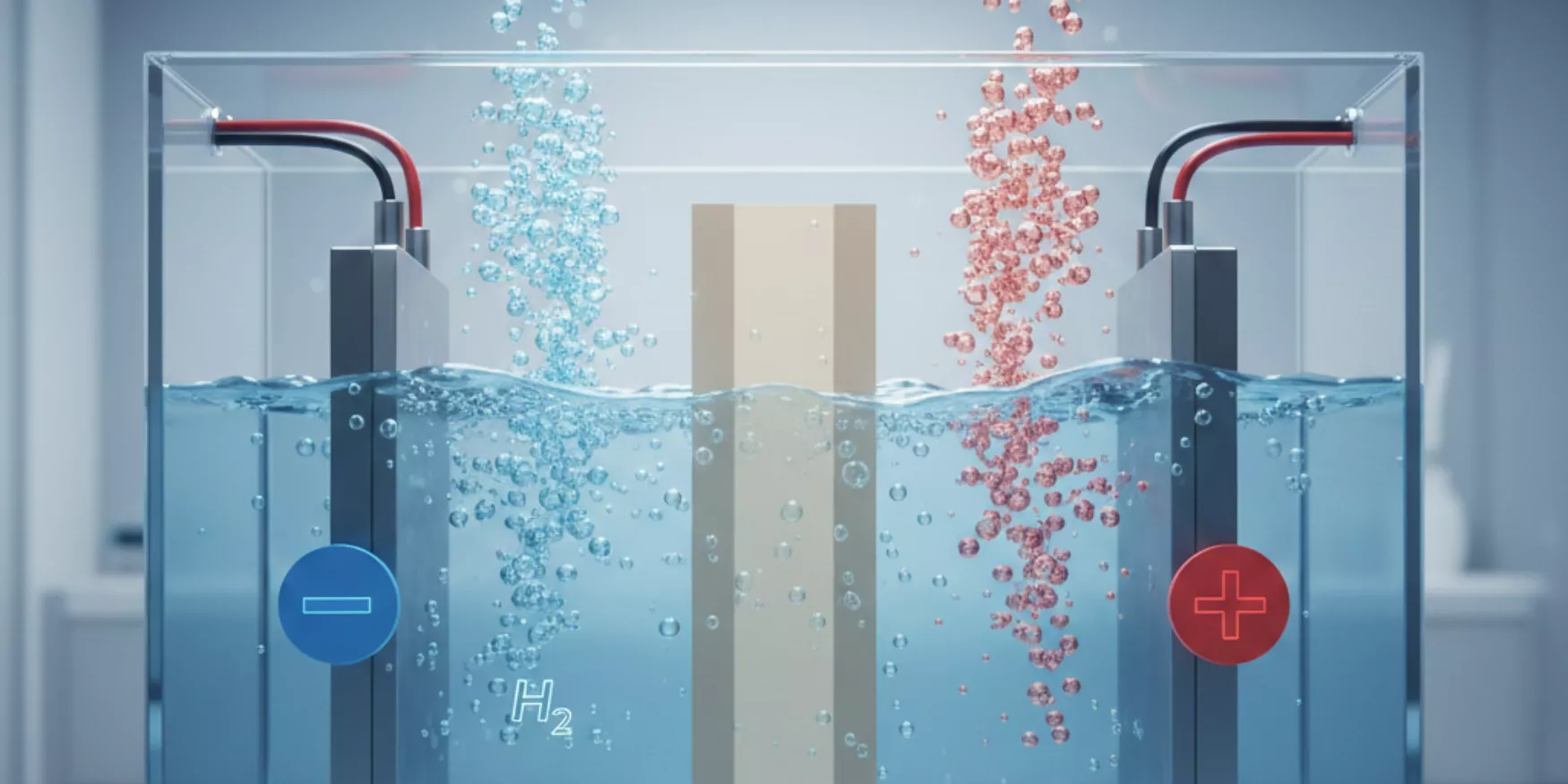
Materia Nova has developed and patented an innovative cell and stack concept—durable, compact, and low‑cost—capable of operating at intermediate temperatures (< 700 °C). This technology enables dynamic operating conditions and extended lifetime while ensuring energy‑efficient hydrogen production.
At the core of our technology, quaternary Ni‑based alloy coatings redefine the standards of electrocatalysis. This advanced material, applied via electrodeposition, provides a controlled microstructure that maximizes the specific surface area. The optimized texture enhances the density of active sites, ensuring higher selectivity and maximum efficiency.
Key Advantages
- Energy Efficiency: Urea oxidation on Ni‑alloy coatings drastically reduces the required electrolysis voltage compared to conventional methods.
- Exceptional Stability: Superior corrosion resistance, specifically engineered for urea‑rich alkaline environments.
- Manufacturing Versatility: A process compatible with both 2D supports (plates) and 3D structures (porous foams).
Our technology is suitable for applications in electrolyzers, fuel cells, hybrid water‑purification and energy‑generation systems, and related hydrogen technologies.
--------------------------------------------
The illustration below highlights selected projects and Materia Nova’s integrated vision to support the development of a sustainable and circular hydrogen value chain, aligned with current environmental requirements.
It is structured around four essential pillars of the hydrogen life cycle.
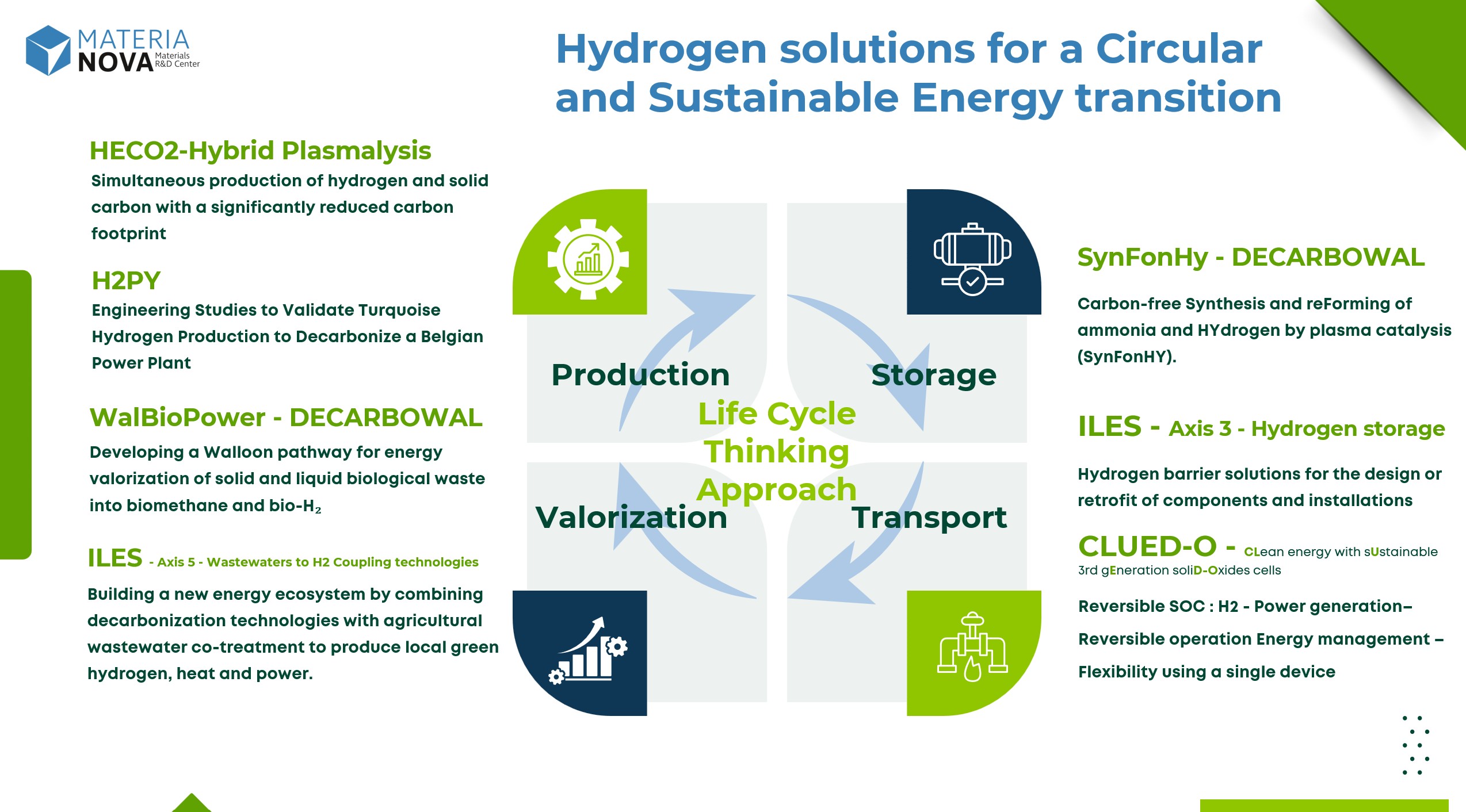
Our Strengths:
- Advanced characterization capabilities (thermal cycling, charge cycling, corrosion stability, degradation mechanisms).
- In‑house Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) expertise.
- Strategic investments in other green hydrogen production routes such as methane plasmolysis, plasma‑assisted biogas treatment, and bioprocesses (Microbial PEM for biofuel/H₂ production).
- Innovations in related fields, including new materials for hydrogen storage and transport, as well as leak‑detection sensors.
- Research and development on both low‑temperature and high‑temperature systems.